What is the Diabetes Honeymoon Phase?
The diabetes honeymoon phase, also known as the remission phase, is a period that sometimes occurs shortly after the diagnosis of type 1 diabetes. It’s a unique and often unexpected period where the body still retains some ability to produce insulin, or the insulin resistance decreases, leading to a temporary reduction in the required insulin dosage. This phase can be a welcome respite for newly diagnosed individuals, offering a chance to manage their condition with fewer insulin injections and a potentially easier time controlling blood sugar levels. The honeymoon phase is not a cure but rather a temporary state of improved glucose control, and understanding it is crucial for effective diabetes management. It’s a time when the pancreas may still be producing some insulin, and the body’s sensitivity to insulin may be temporarily enhanced. This can result in lower insulin requirements and a decreased need for medication, leading to improved overall health and a reduced risk of complications.
Understanding the Mechanisms Behind the Honeymoon Phase
The mechanisms behind the diabetes honeymoon phase are complex, involving a combination of factors that influence insulin production and sensitivity. After the initial autoimmune attack that destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, some beta cells may still be functional or partially damaged but capable of producing some insulin. Additionally, the body’s sensitivity to insulin may temporarily improve, leading to better glucose control. During this phase, the immune system’s attack on the remaining beta cells may slow down, allowing them to function more effectively. This temporary reprieve can result in lower blood sugar levels and a reduced need for insulin injections. It’s important to note that the duration and intensity of the honeymoon phase vary from person to person, depending on factors like age, the severity of the initial diagnosis, and the treatment approach.
The Role of Insulin in the Honeymoon Phase

Insulin plays a crucial role during the diabetes honeymoon phase, even if the need for external insulin injections is reduced. The remaining functional beta cells continue to produce some insulin, but the amount may not be sufficient to regulate blood sugar levels effectively. External insulin may still be needed, but in lower doses. During this phase, the focus shifts towards optimizing the body’s natural insulin production and enhancing insulin sensitivity. Healthcare providers may adjust insulin dosages and treatment plans to match the individual’s needs, helping to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Regular blood glucose monitoring becomes even more important during the honeymoon phase to assess how much insulin is required. Moreover, the goal is to preserve the remaining beta cell function for as long as possible and maintain optimal blood sugar control. This helps reduce the risk of long-term diabetes complications and improves the overall quality of life.
How Long Does the Diabetes Honeymoon Phase Last?
The duration of the diabetes honeymoon phase varies greatly among individuals, with some experiencing it for a few weeks or months, while others can experience it for a year or even longer. There is no fixed timeframe, and the length of the honeymoon phase depends on several factors, including the severity of the initial diagnosis, age, and treatment approach. Some people might experience a rapid decline in insulin production and a quick transition out of the honeymoon phase, while others may have a more prolonged period of remission. It’s important to be prepared for the eventual decline of the honeymoon phase and to be ready to adjust treatment accordingly. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, a healthy lifestyle, and adherence to the prescribed treatment plan are essential to managing diabetes effectively, regardless of the duration of the honeymoon phase. Working closely with a healthcare team can help manage the transition and maintain optimal health.
Factors That Influence the Honeymoon Phase
Several factors influence the onset, duration, and intensity of the diabetes honeymoon phase. Age at diagnosis plays a significant role, with younger individuals often experiencing a longer honeymoon phase than older adults. The initial blood glucose control and the promptness of treatment initiation also affect the duration of the honeymoon phase. Aggressive insulin therapy initiated soon after diagnosis may help preserve beta cell function, potentially extending the honeymoon phase. Other factors like lifestyle choices, including diet and exercise, can also influence the honeymoon phase. A healthy diet, regular physical activity, and stress management techniques can help maintain good blood sugar control and potentially prolong the honeymoon phase. Genetics and individual immune responses also play a role, making the honeymoon phase a unique experience for each person.
Symptoms and Signs of the Honeymoon Phase
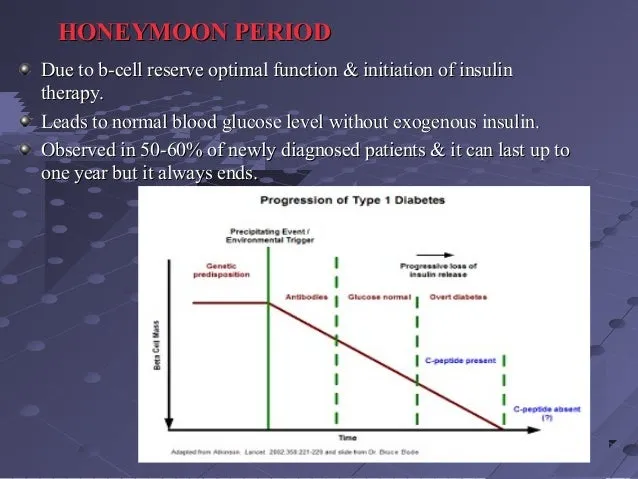
During the diabetes honeymoon phase, individuals may experience specific signs and symptoms that indicate improved blood sugar control and reduced insulin needs. These symptoms may include a decrease in the frequency of insulin injections, improved blood glucose levels, and a reduced need for medication. Many people report feeling better overall, with increased energy levels and a reduction in the common symptoms of diabetes, such as frequent urination, excessive thirst, and fatigue. It’s important to monitor blood sugar levels regularly and be aware of any changes in symptoms or insulin requirements. Noticing these signs is a positive indication of the remission phase, which gives a window to optimize blood sugar management through lifestyle changes and potentially prolong the remission phase.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels During the Honeymoon Phase
Managing blood sugar levels during the diabetes honeymoon phase requires careful monitoring, a balanced approach, and collaboration with your healthcare team. Regular blood glucose monitoring is essential to track blood sugar levels throughout the day and adjust insulin dosages and treatment plans as needed. A healthcare provider may recommend using a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) to monitor blood sugar trends and make timely adjustments. Close collaboration with a diabetes care team is vital to adjust the treatment plan as the honeymoon phase progresses. They can help determine the appropriate insulin doses, medication adjustments, and lifestyle changes required to maintain optimal blood sugar control. This involves monitoring carbohydrate intake, eating balanced meals, and avoiding excessive sugar intake. By keeping blood sugar levels within the target range, individuals can minimize the risk of complications and make the most of the honeymoon phase.
Dietary Adjustments for the Honeymoon Phase
Dietary adjustments are crucial during the diabetes honeymoon phase to maintain optimal blood sugar control and support overall health. Focusing on a balanced diet rich in whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, is essential. Controlling carbohydrate intake is vital, as carbohydrates affect blood sugar levels most. The healthcare team can help determine the appropriate carbohydrate intake for each person based on their individual needs and insulin sensitivity. Limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats is important to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Choosing foods with a low glycemic index (GI) can help prevent blood sugar spikes. Also, consider including foods that are high in fiber to slow down the absorption of sugar, promoting better blood sugar control, and making the most of the honeymoon phase.
Exercise and Physical Activity Strategies

Exercise and physical activity are valuable tools for managing diabetes and supporting the honeymoon phase. Regular exercise enhances insulin sensitivity, helps control blood sugar levels, and supports overall health. Engaging in aerobic exercises like walking, running, swimming, or cycling, can improve insulin sensitivity and help the body use glucose more effectively. Incorporating strength training exercises can help build muscle mass, which can improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control. Before starting any exercise program, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate exercise intensity and frequency based on the individual’s health condition and fitness level. Checking blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise can help determine how the body responds to physical activity and avoid any fluctuations. Regular physical activity, combined with a healthy diet, can help in maintaining optimal blood sugar control during the honeymoon phase.
Medication and Insulin Management
Medication and insulin management are critical components of diabetes care, particularly during the honeymoon phase, where dosages may need adjustment. Healthcare providers will carefully monitor the patient’s blood sugar levels, insulin requirements, and overall health to determine the appropriate medication and insulin dosages. During the honeymoon phase, the need for insulin injections may decrease, and the healthcare provider may adjust the insulin regimen accordingly. Some people might be able to reduce their insulin dosage, while others may temporarily stop taking insulin altogether. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial to ensure that medication and insulin dosages are appropriately adjusted. This may include adjusting the type, dosage, and timing of insulin injections based on individual needs and lifestyle. The goal is to achieve and maintain blood sugar levels within the target range, minimize the risk of complications, and support overall health.
Emotional and Psychological Support
Living with diabetes can be emotionally and psychologically challenging, and it’s essential to seek support during the honeymoon phase. Experiencing a remission phase can bring a mix of emotions, including relief, uncertainty, and anxiety. Seeking support from family, friends, support groups, or a therapist can help individuals cope with these emotions and manage their diabetes more effectively. Joining a diabetes support group can provide a sense of community, allow people to share experiences, and learn from others who understand their challenges. Mental health professionals, such as psychologists or counselors, can help individuals develop coping strategies and manage the stress, anxiety, or depression that may arise. Practicing stress-reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can improve overall well-being. Seeking emotional and psychological support is critical for maintaining a positive outlook and effectively managing diabetes.
When to Seek Medical Advice

Regular medical check-ups and prompt medical advice are essential throughout the diabetes honeymoon phase. Individuals should have regular appointments with their healthcare providers to monitor their blood sugar levels, adjust insulin dosages, and discuss any concerns or changes in their health. It is important to seek medical advice immediately if there are any significant changes in blood sugar levels, new symptoms, or complications. If blood sugar levels consistently fall outside the target range, it is important to consult a healthcare professional. Similarly, any signs of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), such as increased thirst, frequent urination, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, or fruity-smelling breath, require immediate medical attention. Also, any unexplained weight loss, vision changes, or other new symptoms should be reported to a healthcare provider. By working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals can manage their diabetes effectively, minimize the risk of complications, and maintain their overall health.
Long-Term Outlook and Management
The diabetes honeymoon phase is a temporary period, and individuals should prepare for the long-term management of their diabetes. While the honeymoon phase can be a welcome respite, it’s essential to understand that it eventually fades. Continuing the healthy lifestyle habits of the honeymoon phase is important, including following a balanced diet, staying active, and managing stress. Regular blood glucose monitoring remains a cornerstone of diabetes management, allowing adjustments to be made as needed. Education and self-management skills are key to adapting to changes in insulin requirements and managing the condition long-term. Maintaining a strong partnership with the healthcare team ensures that treatment plans remain optimal. By focusing on long-term management, individuals can live full and healthy lives while effectively managing their diabetes.
